Provision EKS with Terraform, Helm and a Load Balancer Controller
Setting up EKS with Terraform, Helm and a Load balancer
Prerequisite
Before we proceed and provision EKS Cluster using Terraform, there are a few commands or tools you need to have in the server where you will be creating the cluster from.
1. awscli - aws-cli/2.12.1 Python/3.11.3
2. go version go1.18.9 linux/amd64
3. Terraform v1.5.0
4. kubectl - Client Version: v1.23.17-eks
5. helm - v3.8.0
Assumptions
The following details makes the following assumptions.
You have aws cli configured
You have created s3 bucket that will act as the backend of the project.
Quick Setup
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/Skanyi/terraform-projects.git
Change directory;
cd terraform-projects/eks
Update the backend.tf and update the s3 bucket and the region of your s3 bucket. Update the profile if you are not using the default profile.
Update the variables.tf profile variable if you are not using the default profile.
If the is a role you want to add to be able to access the EKS cluster created, create the following environment variable.
TF_VAR_rolearn
If there is no role to add, disable adding role to the configmap by commenting out the following field in modules/eks-cluster/main.tf
manage_aws_auth_configmap = true
Initialize the project to pull all the moduels used
terraform init
Validate that the project is correctly setup.
terraform validate
Run the plan command to see all the resources that will be created
terraform plan
When you ready, run the apply command to create the resources.
terraform apply
Detailed Setup Steps.
Creating EKS cluster falls under DevOps Engineer role and sometime it can be very common to create a cluster several times. In this article, I will share how I create EKS cluster using Terraform and Install ALB controller in the cluster. We will also create a sample application that will be exposed using Application load balancer created with Ingress.
Architecture
The following diagram shows the core resources that we will be creating in AWS.
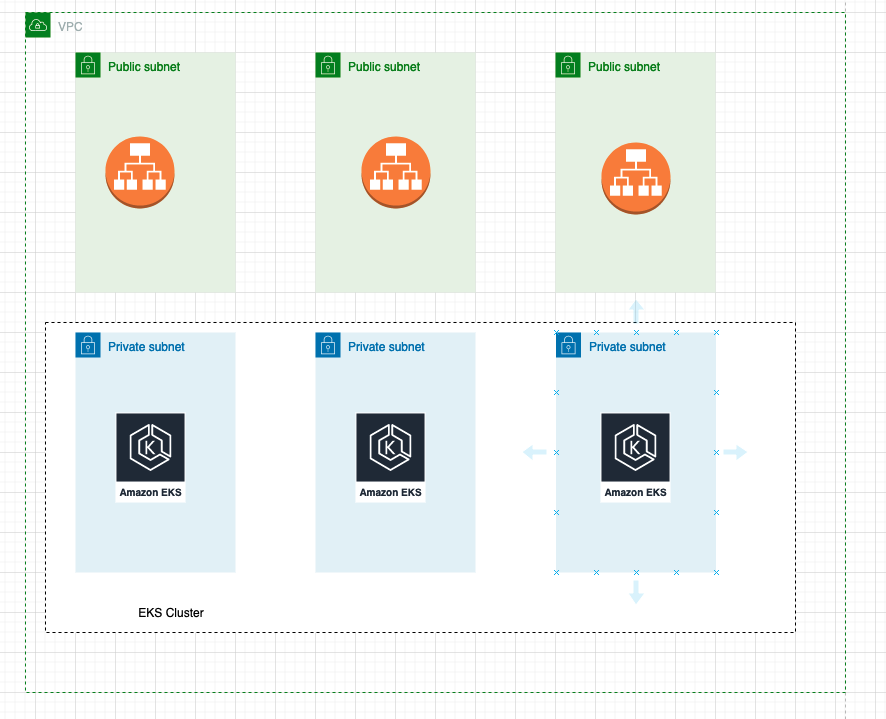
A VPC will be created with three Public Subnets and three Private Subnets in three different Availability Zones. Traffic from Private Subnets will route through the NAT Gateway and traffic from Public Subnets will route through the Internet Gateway.
Kubernetes Cluster Nodes will be created as part of Auto-Scaling groups and will reside in Private Subnets. The Application Load balancer will be created in the Public Subnets.
Setting up EKS
-
Create a VPC where to deploy the cluster. For this I used the VPC module.
module "vpc" { source = "terraform-aws-modules/vpc/aws" version = "5.0.0" name = "eks-vpc" cidr = "10.0.0.0/16" providers = { aws = aws.us-east-2 } azs = ["us-east-2a", "us-east-2b", "us-east-2c"] #private_subnets = [for k, v in local.azs : cidrsubnet(local.vpc_cidr, 8, k)] #public_subnets = [for k, v in local.azs : cidrsubnet(local.vpc_cidr, 8, k + 4)] private_subnets = ["10.0.1.0/24", "10.0.2.0/24", "10.0.3.0/24"] public_subnets = ["10.0.101.0/24", "10.0.102.0/24", "10.0.103.0/24"] enable_nat_gateway = true public_subnet_tags = { "kubernetes.io/role/elb" = 1 } private_subnet_tags = { "kubernetes.io/role/internal-elb" = 1 } tags = { Terraform = "true" Environment = "dev" } } -
Create the EKS cluster using the EKS terraform module
module "eks" { source = "terraform-aws-modules/eks/aws" version = "~> 19.0" cluster_name = "tf-cluster" cluster_version = "1.27" providers = { aws = aws.us-east-2 } cluster_endpoint_public_access = true create_kms_key = false create_cloudwatch_log_group = false cluster_encryption_config = {} cluster_addons = { coredns = { most_recent = true } kube-proxy = { most_recent = true } vpc-cni = { most_recent = true } } vpc_id = var.vpc_id subnet_ids = var.private_subnets control_plane_subnet_ids = var.private_subnets # EKS Managed Node Group(s) eks_managed_node_group_defaults = { instance_types = ["m5.xlarge", "m5.large", "t3.medium"] } eks_managed_node_groups = { blue = {} green = { min_size = 1 max_size = 10 desired_size = 1 instance_types = ["t3.large"] capacity_type = "SPOT" } } tags = { env = "dev" terraform = "true" } }
Adding the Load Balancer Controller
Before we can install the Application load banacer controller, we need to create a role, policy and service account that the controller Will use.
-
We create a role using the module iam-role-for-service-accounts-eks which will create the required policy when attach_load_balancer_controller_policy is set to true.
module "lb_role" { source = "terraform-aws-modules/iam/aws//modules/iam-role-for-service-accounts-eks" role_name = "${var.env_name}_eks_lb" attach_load_balancer_controller_policy = true oidc_providers = { main = { provider_arn = var.oidc_provider_arn namespace_service_accounts = ["kube-system:aws-load-balancer-controller"] } } } -
We create a service account that is annotated with the role created in the above step.
resource "kubernetes_service_account" "service-account" { metadata { name = "aws-load-balancer-controller" namespace = "kube-system" labels = { "app.kubernetes.io/name" = "aws-load-balancer-controller" "app.kubernetes.io/component" = "controller" } annotations = { "eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn" = module.lb_role.iam_role_arn "eks.amazonaws.com/sts-regional-endpoints" = "true" } } } -
Finally we install the AWS load balancer controller.
resource "helm_release" "alb-controller" { name = "aws-load-balancer-controller" repository = "https://aws.github.io/eks-charts" chart = "aws-load-balancer-controller" namespace = "kube-system" depends_on = [ kubernetes_service_account.service-account ] set { name = "region" value = var.main-region } set { name = "vpcId" value = var.vpc_id } set { name = "image.repository" value = "602401143452.dkr.ecr.${var.main-region}.amazonaws.com/amazon/aws-load-balancer-controller" } set { name = "serviceAccount.create" value = "false" } set { name = "serviceAccount.name" value = "aws-load-balancer-controller" } set { name = "clusterName" value = var.cluster_name } }
Cleanup the Resources we Created
When we are done testing the setup and don’t require the resources created anymore, we can use the steps below to remove them.
1.1 terraform init
1.2 terraform destroy
If you get errors deleting the resources, remove the .terraform folder and destroy again.
2.1 rm -rf .terraform
2.2 terraform destroy
Conclusion of Terraform Kubernetes Deployment
Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) is a managed Kubernetes service provided by AWS, which takes the complexity and overhead out of provisioning and optimizing a Kubernetes Cluster for development teams.
An EKS Cluster can be created using a variety of methods; nevertheless, using the best possible way is critical in improving the infrastructure management lifecycle.
The above method is just one of the method that can be used to create the EKS clusters.
Next Steps
The following project deploys a sample nginx application and create a load balancer that can be used to access the application.
Deploy sample application and create a Load Balancer Using Terraform to EKS Cluster
Throughout the following setup, I referenced heavily from the following sources.
[1] AWS VPC Terraform module - https://registry.terraform.io/modules/terraform-aws-modules/vpc/aws/latest
[2] AWS EKS Terraform module - https://registry.terraform.io/modules/terraform-aws-modules/eks/aws/latest
[3] IAM Role for Service Accounts in EKS - https://github.com/terraform-aws-modules/terraform-aws-iam/tree/master/examples/iam-role-for-service-accounts-eks